Understanding Pancreatic Surgery: Benefits, Risks, and Relevant Anatomy
*Please note: This slide set represents a visual interpretation and is not intended to provide, nor substitute as, medical and/or clinical advice.
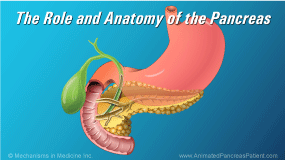
The pancreas is an important organ in the digestive system.
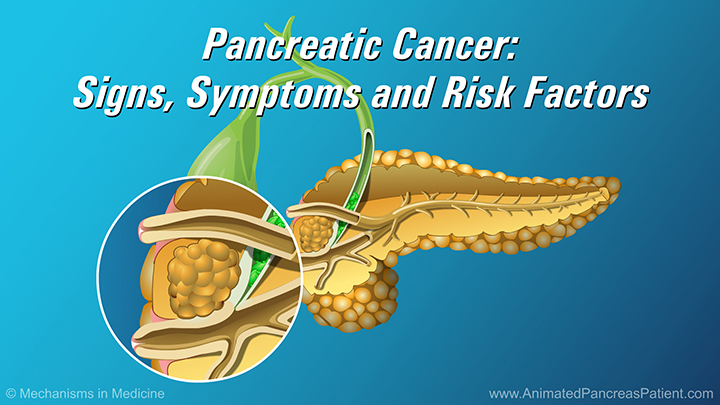
It can be affected by episodic flare ups of acute or chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cysts, and pancreatic cancers.
More than one of these conditions may manifest in the same patient at one time.
In cases of localized pancreatic cancer or obstructions that block the flow of digestive fluids from the pancreas, your doctor may recommend removing the pancreas, or part of the pancreas, through surgery.
Pancreatic surgery can have several goals, including:
- relieving pain
- enhancing digestive function, and preventing further decline of function
- and removing pancreatic cysts or tumors
The pancreas is located in an anatomically complex region of the body, where neighboring organs are closely associated…
…and share the same blood supply. As a result, pancreatic surgeries usually involve the removal of several organs together.
Tumors, cysts and obstructions in the head of the pancreas are removed using a surgery known as the Whipple procedure.
In a classic Whipple procedure, the head of the pancreas, part of the stomach, part of the bile duct, and some of the small intestine are removed.
In some cases, a pylorus-preserving Whipple procedure may be used, where the stomach is left intact. Both are equally effective.
In both variations of the Whipple procedure, the remaining body and tail of the pancreas, the remaining bile duct, and the stomach are reconnected to the small intestine.
Tumors, cysts and obstructions in the body or tail of the pancreas are removed using a procedure called a distal pancreatectomy.
In a distal pancreatectomy, the affected portion of the pancreas and often the spleen are removed.
To complete the procedure, the cut end of the pancreas is stapled or sutured closed.
A total pancreatectomy is used when the entire pancreas must be removed. This includes several scenarios such as: Centrally located tumors in the neck of the pancreas and large or multiple tumors, severe chronic pancreatitis, and certain cystic diseases such as main-duct or mixed-variant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN).
In a total pancreatectomy, the entire pancreas is removed together with the duodenum, the gallbladder and part of the bile duct, and the spleen.
To complete the procedure, the remaining bile duct and the stomach are reconnected to the small intestine.
Following surgery, you may lose certain body functions that were performed by the tissues and organs that were removed. Most of these losses can either be treated or managed.
After a Whipple procedure, there are usually no functional losses associated with removing the gallbladder or a portion of the bile duct. However, you may develop diabetes and you may experience the presence of fat in your stool (called steatorrhea). You may also experience a reduction in nutritional absorption.
After a distal pancreatectomy, you may develop diabetes, and may experience steatorrhea. You may also experience changes in your platelet count, and be more prone to certain infections, for which you will be vaccinated.
After a total pancreatectomy, you may experience all of the changes associated with the Whipple procedure and distal pancreatectomy, but you will also experience complete loss of pancreatic function, including insulin and enzyme production.
In certain cases, total pancreatectomy can be combined with transplantation of insulin-producing islets, which are separated from the removed pancreas and transplanted into the liver. This additional procedure may reduce or eliminate the need for insulin injections.
Pancreatic surgeries can be performed safely and effectively, and are well tolerated by patients. The benefits of surgery generally outweigh the functional losses, which can be routinely and effectively managed.
For the best possible outcomes, seek out an experienced surgeon at a multidisciplinary care center that specializes in pancreatic surgery.